[many definitions borrowed from Jon Storm]
ADSL – (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) A method of connecting a computer to the internet over a standard voice phone line using ethernet office networking technology. Most broadband connections work this way. Asymmetric because it is faster from internet to PC than the other way.
BIOS – (Basic Input/Output System) A program built into every PC for setting up very basic things, like how many hard and floppy disks you have and what type they are; the first thing that loads when you start your PC. You usually only need to access the BIOS if you are upgrading your hardware, eg adding more RAM or an extra disk drive, or setting a power-on password. BIOS settings are stored in a special type of memory called CMOS.
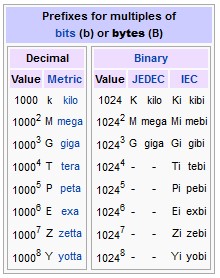
Bit – The smallest unit of information in a computer, can either equal 0 or 1. Eight bits equal one byte.
bps – (Bits Per Second) A measure of how quickly information is being transferred, usually via a modem or network. Divide by ten to get an approximation of the number of characters per second (cps).
Byte – A basic unit of measurement for pieces of information; the space required to store one character.
CD-ROM – (Compact Disk-Read Only Memory) A misnomer, as strictly speaking it is not memory but storage. Identical to standard music CDs. A popular medium for releasing programs. Now being replaced by DVD, which has a much higher capacity.
CMOS – (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) A special type of memory which retains its data when the PC is switched off, used to store settings for things like what type of hard disk you have, and how much memory. The settings are accessed via the BIOS.
CODEC – (COmpressor/DECompressor) A small piece of computer code that tells the computer how to decode particular types of information, usually video files. If your video player won’t play a particular format, you can usually download and install a codec which will tell it how from the internet.
CPU – (Central Processing Unit) The nerve center of the computer : everything flows through it. Often just called “the processor”. The best known PC processors are Intel’s Pentium (oh yeah, and AMD).
DIMM – (Dual In-line Memory Module) A module of RAM (memory) for a PC.
DVD – Short for digital versatile disc or digital video disc, a type of optical disk technology similar to the CD-ROM. A DVD holds a minimum of 4.7GB of data, enough for a full-length movie.
DVI – (Direct Video Interface) A special type of connector for computer monitors, particularly flat panels.
I/O – (Input/Output) Classic analogy – ‘garbage in, garbage out’.
IDE – (Integrated Drive Electronics ) A type of PC hard disk, now obsolete.
Motherboard – The main circuit board in the computer – all the other bits and pieces are plugged into it.
Northbridge – The northbridge or host bridge was one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a PC motherboard, used to manage data communications between a CPU and a motherboard. It is supposed to be paired with a second support chip known as a southbridge.
OCR – (Optical Character Recognition) A program which attempts to convert a scanned image (ie a picture) of text into text that can be edited in a word processor. The result is rarely 100% accurate and must be carefully proofread, but it can save a lot of retyping.
OS – (Operating System) Every computer has an operating system, which is a sort of master program that runs automatically when you switch the computer on, and continues running till you switch off. It is responsible for the many routine tasks required to keep a computer running: moving the pointer when you move the mouse, providing icons and menus, running other programs such as a word processor or a game which you may request, controlling the various disk drives, the screen, etc.
PC – (Personal Computer) Originally just short for “personal computer”, PC is now an industry standard, partly evolved in the marketplace, partly agreed by a committee of the major players in the computer industry.
PCI – (Peripheral Component Interconnect) A standard for PC expansion cards, currently the most popular in desktop PCs. A “PCI slot” is a socket on the motherboard for such cards.
PDF – (Portable Document Format) A popular document format, used mainly for online computer manuals, which retains the look of a printed book onscreen.
RAM – (Random Access Memory) The computer’s main memory, which it uses to hold whatever you are currently working on. The contents of RAM are lost when the computer is switched off. Adding more RAM is often the most cost-effective upgrade for an ageing computer.
SATA – (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) A high speed standard for connecting hard disks to your computer, replacing (E)IDE on most new computers.
Scanner – A device which makes high-resolution copies of printed images and text to use on a computer.
Software – The programs that run on a computer. Without software, a computer can’t do anything.
Southbridge – The southbridge is one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a personal computer motherboard, the other being the northbridge. The southbridge typically implements the slower capabilities of the motherboard in a northbridge/southbridge chipset computer architecture.
SSD – (Solid State Drive) A technology that replaces the conventional hard disk, particularly in laptops, with a device that behaves exactly like a hard disk but uses memory instead of magnetic storage. It is very much faster than even the fastest hard disks and is now standard on high-end laptops and notebooks, and often retrofitted into PCs as well.
(persistent) Storage – The generic term for any method of storing information which is not lost when the computer is switched off; the most common types are hard disks, CDs, and DVDs.
Streaming – Video or audio that plays while still downloading, rather than you having to wait till the download has finished.
Surfing – In a computer context, wandering around the World Wide Web (which really annoys the guys with the boards and the big waves ‘cause so little effort’s involved). Also called websurfing.
URL – (Universal Resource Locator) An address used to locate something on the internet, most often a web page. All web addresses are URLs.
USB – (Universal Serial Bus) A standard type of connection port, used to attach extra devices such as a scanner to a computer. Standard on new PCs from around 1998. USB 2.0 and 3.0 are faster versions of the same thing. Many PCs now use USB to connect the mouse and keyboard.
VGA – (Video Graphics Array) An early colour graphics standard for PCs, now used as a sort of lowest common denominator which all monitors and graphics cards understand.
Virus – A program that has been deliberately created to cause computer problems, usually minor ones as a prank, but occasionally very nasty ones, such as erasing your entire hard disk. Viruses were originally designed to attach themselves to programs on a disk, and then “hide” in the computer’s memory once the host program is executed, and “infect” every disk they come across.
VOIP – (Voice Over Internet Protocol) A system for making cheap phone calls over the internet instead of via the telephone system.
WiFi – (WIreless FIdelity) A method of connecting computers to a network without cables, using small radio transmitter/receivers built in to most portable devices and broadband modems. Many hotels and other public locations now offer free WiFi if you have a suitable device, such as a laptop, tablet or smartphone.